Categories
Latest blog
Arc Spark Optical emission Spectrometer-Introduction to CCD Photoelectric Detector
Jun 06 , 2025Arc Spark Optical emission Spectrometer-Introduction to CCD Photoelectric Detector
Traditional spectral detection system for the monochromator plus photomultiplier tube (PMT) Since the 1970s, it is desired to use photodiode arrays (SPDA) and other photoelectric sensors to establish a three-dimensional spectral map, and develop the corresponding processing technology. SPDA not only can obtain a certain range of detection information in the wavelength range, but also has the flexibility of integration capabilities, but it is not as sensitive and dynamic range as PMT, and the noise is larger, the linear range is narrow, and the dark current is also large, while the CCD makes up for these shortcomings.
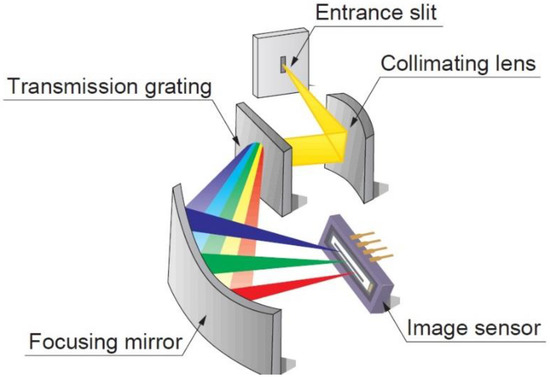
There are several properties of CCD that are closely related to spectrometer instruments:
(1) High sensitivity and low noise. CCD devices have a very high quantum efficiency, at least 10%, up to 90% or more. Its charge transfer efficiency of almost 100%, it works at low temperatures almost no dark current, the noise is almost close to zero, the latest CCD devices, has achieved a very high signal-to-noise ratio at room temperature, very low dark current, fully meet the requirements of the instrument in the analysis of the constant and micro-analysis. The above advantages make the sensitivity of CCD devices exceed that of other detectors (e.g. PMT and SPDA), and the lower limit of detection reaches pg level or even fg level.
(2) Wide spectral range (200~1050nm). Quantum efficiency can be as high as 90 % in the visible region (400~500nm) and at least 10 % between the far ultraviolet region (200nm) and the near infrared (1000nm). In the 100 ~ 1100nm wide spectral region, CCD have high quantum efficiency, and most of the emission, absorption and scattering spectral instruments are working in this region, so the CCD has become an ideal detector for all kinds of spectral instruments.
(3) Wide dynamic linear response range of 10 magnitudes. The CCD has a wide response range and ideal response linearity of 10 magnitudes, and maintains a linear response throughout the dynamic response range, which is of particular significance for quantitative spectral analysis.
(4) Geometric stability, resistance to overexposure: CCD is stable in its geometric, thermal and electrical properties after a long period of operation, and is not afraid of overexposure, so it is stronger and more durable than PMT.
(5) Multiple channels can be sampled simultaneously to obtain a three-dimensional wavelength-intensity-time spectrogram, which can be used in conjunction with a photocathode device to observe X-ray images.
These characteristics of CCD make it an ideal detector for spectrometers. In the last two Pittsburgh conferences, a series of research reports were presented on CCD detectors for emission spectrometers, Raman spectrometers, fluorescence spectrophotometry, etc. It is expected that CCD will become a detector for all kinds of spectral instruments in a few years to replace the photomultiplier tubes.